Sampling
The Sampling options in the CPillar Project Settings dialog allow you to choose:
- Sampling Method
- Number of Samples
for a Probabilistic Analysis in CPillar.
Sampling Method
The Sampling Method determines how the statistical input distributions for the Random Variables you have defined for a Probabilistic Analysis, will be sampled. Two Sampling Methods are available in CPillar:
- Monte Carlo
- Latin Hypercube
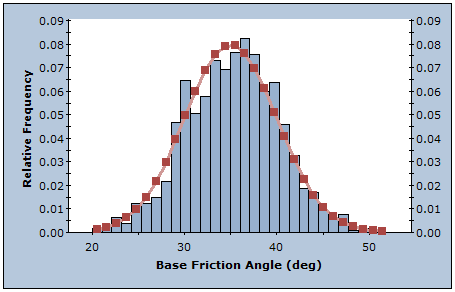
Monte Carlo Method
The Monte Carlo sampling technique uses random numbers to sample from the input data probability distributions. Monte Carlo techniques are commonly applied to a wide variety of problems involving random behavior in geotechnical engineering.
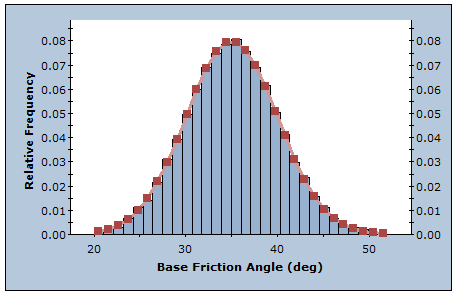
Latin Hypercube Method
The Latin Hypercube sampling technique gives comparable results to the Monte Carlo technique, but with fewer samples [Iman et. al. (1980), Startzman et. al. (1985)]. The method is based upon "stratified" sampling with random selection within each stratum. This results in a smoother sampling of the probability distributions. Typically, an analysis using 1000 samples obtained by the Latin Hypercube technique will produce comparable results to an analysis of 5000 samples using the Monte Carlo method [Hoek et. al. (1995)].
Number of Samples
The Number of Samples which will be generated for each random variable, for a Probabilistic Analysis. For example, if Number of Samples = 1000, then 1000 values of each input data random variable (e.g. Pillar Length) will be generated, according to the Sampling Method and statistical distribution for each random variable. The analysis will then be run 1000 times, and a safety factor calculated for each set of input data samples. This results in a distribution of safety factors, from which the Probability of Failure (PF) is calculated.