Random Variables
In order to carry out a Probabilistic Analysis with RocSlope2, you must define at least one input parameter as a random variable.
Input parameters with a probability distribution function icon can be defined as random variables. Users can choose among a list of Statistical Distributions (e.g. Normal, Uniform, etc.) and enter the corresponding statistical properties of the distribution.
- Ensure that the project's Analysis Type is set to Probabilistic Analysis. See the Statistics topic for more information.
- In one of the applicable input dialogs, enter the desired value for the input parameter.
- See the following topics for more information on parameters which can be defined as random variables in a RocSlope2 Probabilistic Analysis:
- See the following topics for more information on parameters which can be defined as random variables in a RocSlope2 Probabilistic Analysis:
- The applicable parameters will have Distribution icons
 next to them. Click the icon to open the Statistical Distribution parameters popup.
next to them. Click the icon to open the Statistical Distribution parameters popup. - Select the desired distribution and enter the required details. Select OK to close the popup.

In addition, if you are using the Persistence Analysis option, you can define the following random variables:
- Joint Persistence, or
- Trace Length
See the Joint Persistence Analysis topic for more information.
For information about the selection of statistical distributions, standard deviation and minimum/maximum values, see the Statistical Distributions Overview topic.
How Random Variables are Used in the Analysis
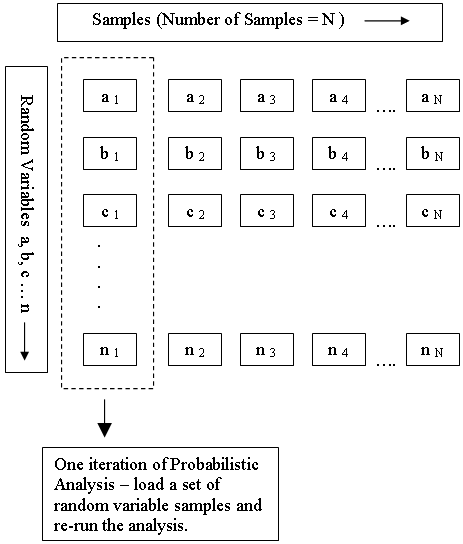
Each input parameter defined as a random variable is sampled according to the selected statistical distribution, the Sampling Method and the Number of Samples (chosen in Project Settings). This generates N values of each random variable (where N = Number of Samples).
As shown in the following diagram, each iteration of the Probabilistic Analysis is carried out by loading a new set of random variable samples and re-running the analysis. This is repeated N times where N = Number of Samples.
Random Variable Samples used in Probabilistic Analysis