Permeability Models
The following models are provided in the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog for describing the permeability in the unsaturated zone as a function of matric suction.
- Simple
- Fredlund and Xing
- van Genuchten
- Brooks and Corey
- Gardner
- Constant
- User Defined
Plot Function 
This option, available for all permeability models except for Constant, plots relative permeability and relative water content as functions of matric suctions (SWCC) based on the selected model and entered parameters. Relative permeability is the ratio of current to maximum permeability, while relative water content is the ratio of current to maximum water content.
For User Defined models, this option accounts for and is available after Define Permeability and Water Content Functions. Note that the Relative Ks and Relative WC inputs are not included here.
Pick button ![]()
This option is available for Fredlund and Xing, van Genuchten, Brooks and Corey, and Gardner models. If you select the Pick button you will see another dialog, from which you can select from a list of materials, with representative parameters for the selected model. (References for the data are provided in the dialog). If you select [OK] in this dialog, the currently selected parameters will be automatically loaded into the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog.
Simple
With the Simple model, an unsaturated permeability function is automatically determined by RS2 based on the magnitude of the saturated permeability Ks and the selected Soil Type. To view the function determined by RS2, you can select the Plot button in the dialog. For the Simple model, you can choose one of the following Soil Types:
- General
- Sand
- Silt
- Clay
- Loam
For the General soil type, the unsaturated permeability simply decreases by an order of magnitude within the initial range of matric suction values, and then remains constant for higher values of suction.
For specific soil types (Sand, Silt, Clay or Loam) average curves have been determined from typical literature values.
Fredlund and Xing
The following equation defines the Fredlund-Xing permeability function (Fredlund and Xing, 1994):
![]() Eqn.2
Eqn.2
where: A, B and C are the model parameters
![]() = 2.7182818 …
= 2.7182818 …
![]() = matric suction
= matric suction
K = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
Van Genuchten
The following equations define the van Genuchten permeability function (van Genuchten, 1980):
![]() Eqn.4a
Eqn.4a
![]() Eqn.4b
Eqn.4b
where: ![]() = degree of saturation
= degree of saturation
h = pressure head (suction)
![]() are the model parameters
are the model parameters
K = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
NOTE: the parameters m and n are related as follows:
![]() Eqn. 4c
Eqn. 4c
However, you can specify a value of m which is independent from n, by selecting the Custom m check box, and entering a value for m.
Brooks and Corey
The following equations define the Brooks-Corey permeability function (Brooks and Corey, 1964):
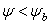 :
: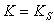 Eqn.1a
Eqn.1a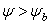 :
: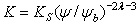 Eqn.1b
Eqn.1b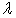 = Pore size index
= Pore size index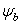 = bubbling pressure
= bubbling pressure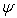 = matric suction
= matric suctionK = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
Gardner
The following equation defines the Gardner permeability function (Gardner, 1956):
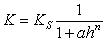 Eqn.3
Eqn.3where: a and n are the model parameters
h = pressure head (suction)
K = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
Constant
For the Constant model, the permeability is always equal to the defined saturated permeability (Ks).
User Defined
This model provides complete flexibility in customizing permeability functions, with two steps:
- Define Permeability and Water Content (required): define both functions based on matric suctions.
- Relative Ks and Relative WC (optional): set spatial distributions which will act as multipliers on the values from the last step.
The final permeability and water content are calculated as:
- permeability = Input permeability (from step 1) * Relative Ks (from step 2)
- water content = Input water content (from step 1) * Relative WC (from step 2)
Define Permeability and Water Content
The permeability and water content functions (SWCC) are plotted by user input data. Select the Pencil ![]() icon of the section. In the prompted User Defined Permeability and Water Content dialog, you can define both a) permeability vs. matric suction and b) water content vs. matric suction functions, as follows:
icon of the section. In the prompted User Defined Permeability and Water Content dialog, you can define both a) permeability vs. matric suction and b) water content vs. matric suction functions, as follows:
- In the User Defined Permeability and Water Content dialog, Enter a Name for the function.
- Select the Permeability tab and enter the Matric Suction and Permeability values in the grids. A graph of the data will be displayed at the right of the dialog.
The water content can be defined either by water content OR by degree of saturation:
- From the WC Input Type dropdown list at the top, choose either By Water Content OR By Degree of Saturation.
- Your selection will lead you to the Water Content OR Degree of Saturation tab.
- Under the tab, enter the Matric Suction and Water Content OR Degree of Saturation values in the grids. A graph of the data will be displayed at the right of the dialog.
- When all data has been entered, select the OK button to save change and exit dialog. To exit dialog without saving changes, select the Cancel button.
- In the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog, from the User Define Permeability and Water Content drop-list, select a desired function to use.
In the User Defined Permeability and Water Content dialog, you can add  , delete
, delete  , rename
, rename  , or copy a function. The function can also be Imported
, or copy a function. The function can also be Imported  from or exported
from or exported  to a separate file, with a .FN5 filename extension.
to a separate file, with a .FN5 filename extension.
 , cut
, cut  , copy
, copy  , paste
, paste  , insert row
, insert row  , delete row
, delete row  , and append row
, and append row  . If you have data copied, and want to paste to the grid. Click on the select all button
. If you have data copied, and want to paste to the grid. Click on the select all button  , and click paste
, and click paste  or ctrl+v. Data will be pasted to the grid.
or ctrl+v. Data will be pasted to the grid.The Copy Chart option to the top of the graph will copy a bitmap image of the current plot view to your clipboard. You can then paste the image into another application.
Relative Ks
This section is optional, and it allows only spatial distributions. Here, the Ks will be defined as a factor relative to the Ks value in the Define Permeability and Water Content function, rather than as an absolute value.
Relative WC
This section is optional, and it allows only spatial distributions. Here, the water content (or degree of saturation) will be defined as a factor relative to the water content (or degree of saturation) value in the Define Permeability and Water Content function, rather than as an absolute value.
The lower bound condition for Relative WC / DoS must be satisfied. Otherwise, an error message with calculated value will display: “At least one function value must be less than porosity / (wc * wc stage factor) = (X)”.