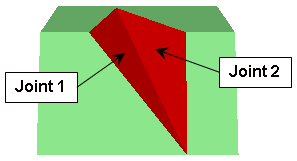
Joint Orientations
The SWedge analysis requires TWO (or three) distinct joint plane orientations to be defined. The joint plane orientations must intersect the slope planes in a kinematically admissible manner, such that a wedge is formed which is capable of being removed from the slope.
Joint Orientations in SWedge are always defined by Dip and Dip Direction.
To define the joint orientations:
- Select Input Data
 from the toolbar or the Analysis menu.
from the toolbar or the Analysis menu. - Select the appropriate tab(s) in the Input Data dialog and enter the joint orientations:
- For a Deterministic Analysis, enter the Dip and Dip Direction for Joint 1, Joint 2 and Basal Joint (if defined).
- For a Probabilistic Analysis, it is possible to define statistical variability of the joint plane orientations. See the Probabilistic Joint Orientations topic for more information.
- For a Combination Analysis, any number of joint plane orientations can be defined, and SWedge will analyze all possible combinations of two (or three) joints. See the Combination Joint Orientations topic for more information.
Waviness Angle
A "waviness angle" may be defined for the joint planes, for Deterministic or Probabilistic analysis. Although the waviness angle is grouped with the joint plane orientation information in the Input Data dialog, the waviness angle only affects the shear strength of the joint planes. It does NOT affect the wedge geometry. For the purpose of calculating the wedge geometry, the joint planes are always assumed to be perfectly flat. For details about the waviness angle implementation in SWedge see the Waviness Angle topic.
Import from Dips
It is also possible to import joint orientations from a Dips file. See the Import from Dips topic for details.