12 - Automate Deterministic Analysis
1.0 Introduction
The Automate Compute option helps users quickly generate results for several SWedge analysis cases at a time by reading in various model inputs from Excel. In this tutorial, we familiarize you with the Automate Compute feature by automating the computation of three unique Deterministic analysis cases (i.e., three wedges).
Topics Covered in this Tutorial:
- Deterministic Analysis SWedge Model
- Input Excel File Format
- Adding Input Excel File(s) to Automate Compute File Queue
- Output SWedge Automate Compute Results File
- SWedge Automate Compute Error Log
Finished Product:
The finished products of this tutorial can be found in the Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic Analysis folder, located in the Examples > Tutorials folder in your SWedge installation folder. Inside, you will find:
- Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic_base file.swd7 SWedge model file setup for automation
- Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic_inputs.xlsx Excel input file
- Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic_inputs folder containing the computed results files
2.0 Creating a New File
- If you have not already done so, run the SWedge program by double-clicking the SWedge icon in your installation folder or by selecting Programs > Rocscience > SWedge > SWedge in the Windows Start menu.
When the program starts, a default model is automatically created. If you do NOT see a model on your screen:
- Select: File > New

Whenever a new file is created, the default input data forms valid slope geometry, as shown in the image below.
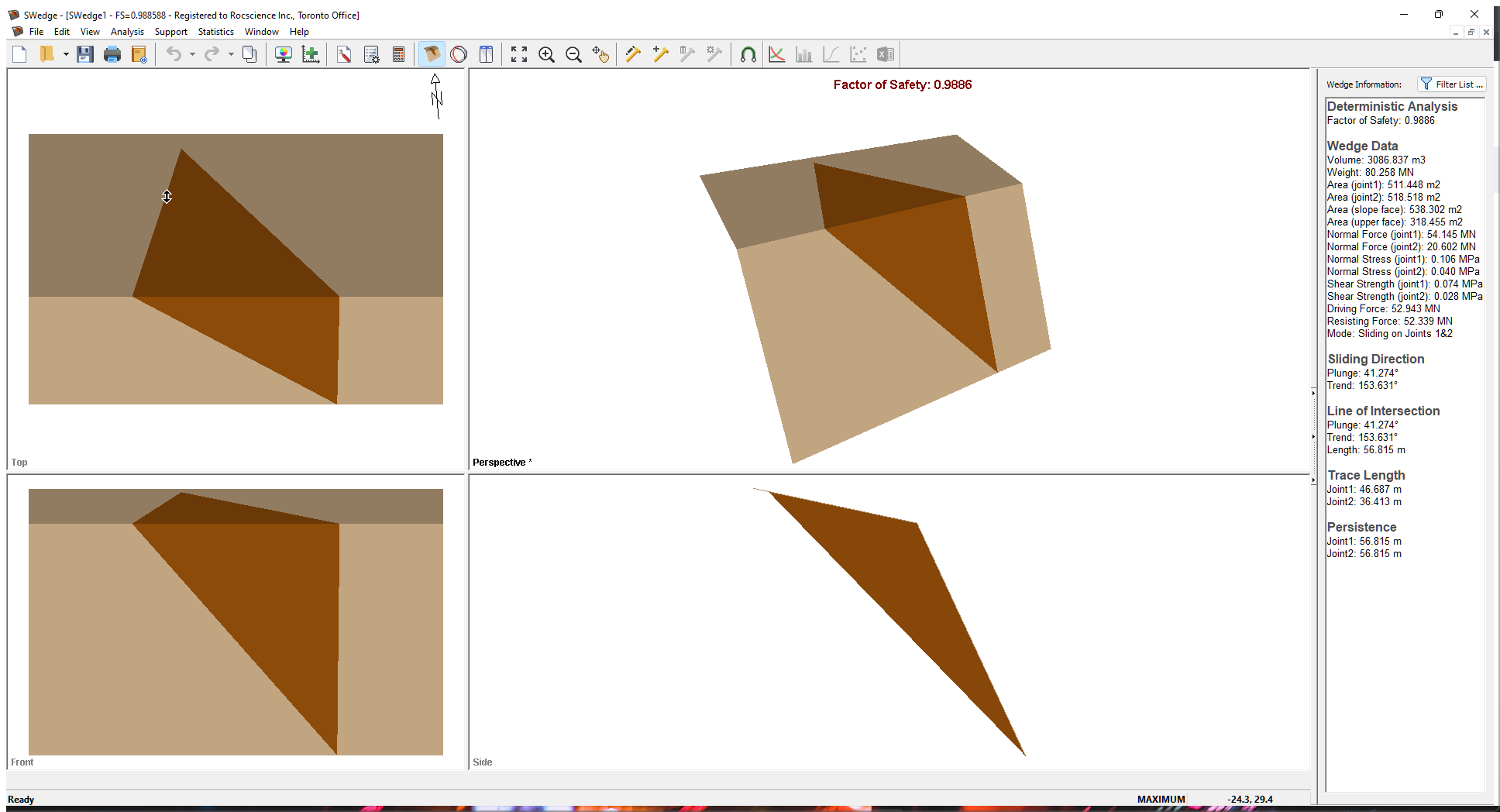
If the SWedge application window is not already maximized, maximize it now so that the full screen is available for viewing the model.
Before we are ready to run Automate Compute, we must first set up the model environment in the following dialogs:
- Project Settings
- Input Data
- Scale Wedge
3.0 Project Settings
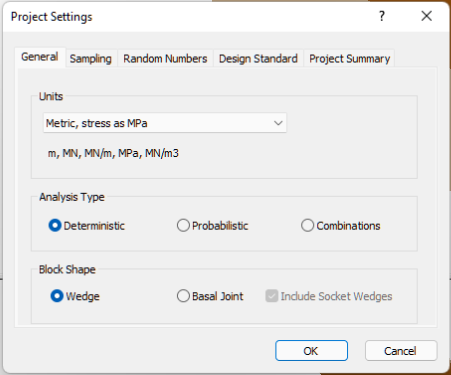
First, set the model Units, Analysis Type, and Block Shape.
- Select Project Settings
 from the Analysis menu to open the Project Settings dialog.
from the Analysis menu to open the Project Settings dialog. - Set the Units = Metric, stress as MPa
- Set the Analysis Type = Deterministic
- Set the Block Shape = Wedge
- Select OK to close the dialog.
4.0 Input Data
Next, set the optional input data.
- Select Input Data
 from the Analysis menu to open the Deterministic Input Data dialog.
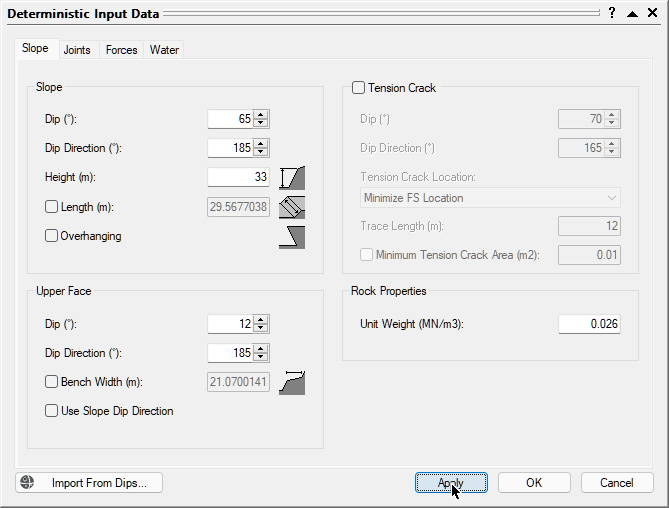
from the Analysis menu to open the Deterministic Input Data dialog. - Open the Slope tab.
We will keep all the check box controls in the default state. Keep in mind that the following are required input parameters that have to be specified later on in the Input Excel File:- Slope Dip
- Slope Dip Direction
- Slope Height
- Upper Face Dip
- Upper Face Dip Direction
- Rock Unit Weight
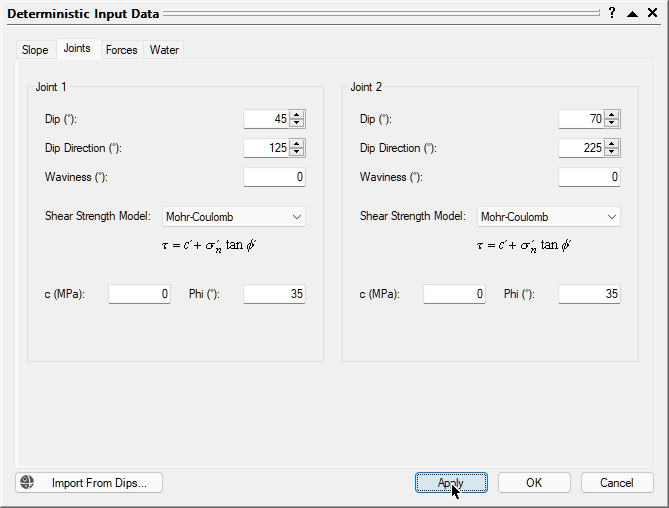
- Open the Joints tab.
- Set Joint 1 Shear Strength Model = Mohr-Coulomb
- Set Joint 2 Shear Strength Model = Mohr-Coulomb
- Joint 1 Dip
- Joint 1 Dip Direction
- Joint 1 Waviness
- Joint 1 Cohesion
- Joint 1 Friction Angle
- Joint 2 Dip
- Joint 2 Dip Direction
- Joint 2 Waviness
- Joint 2 Cohesion
- Joint 2 Friction Angle
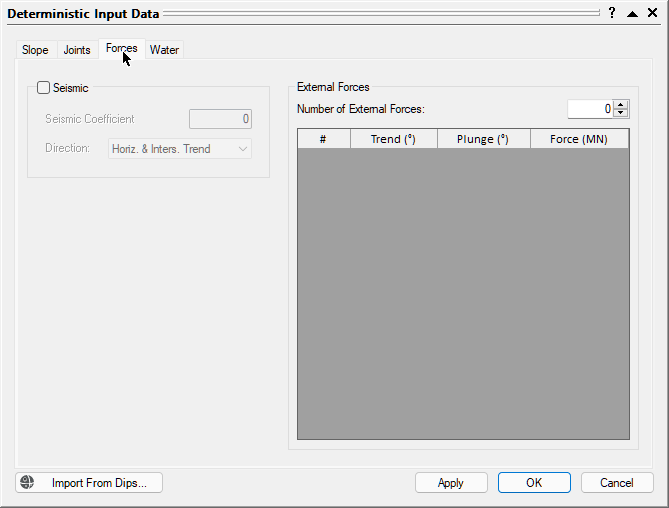
- Open the Forces tab.
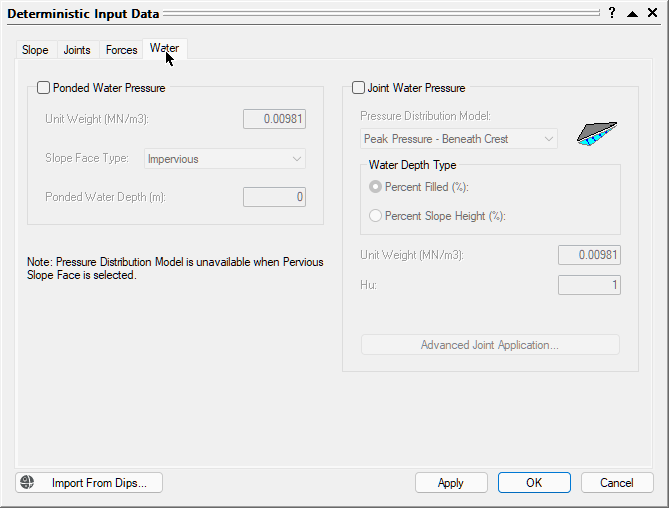
- Open the Water tab.
- Select OK to close the dialog.
We will keep all the check box and combo box controls in the default state. Keep in mind that the following are required input parameters that have to be specified later on in the Input Excel File:
We will leave all the check box controls in the default state (unchecked). No input parameters are required since no Seismic or External Forces are applied.
We will leave all the check box controls in the default state (unchecked). No input parameters are required since no Ponded Water Pressure or Joint Water Pressure are applied.
5.0 Input Excel File
Now, let's take a look at the structure of the input Excel file.
- Obtain the SWedge Deterministic Excel Template by selecting Analysis > Automate Compute > Deterministic Excel Template from the menu.
- Create a folder called Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic.
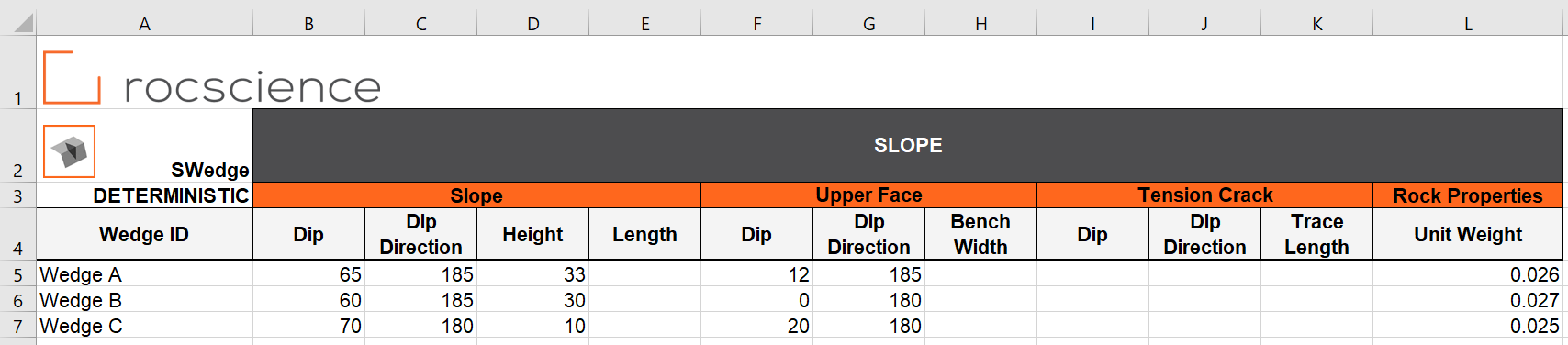
- Navigate to the SLOPE worksheet.
- Under the Wedge ID column, provide the names of the wedges. We will name them arbitrarily Wedge A, Wedge B, and Wedge C. Each row in the input Excel file represents one Deterministic Analysis case in SWedge.
- Enter the following:
- Navigate to the JOINTS worksheet.
- Under the Wedge ID column, provide the names of the wedges (Wedge A, Wedge B, and Wedge C ).
- Enter the following:
- Save the Excel file as Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic_inputs.xlsx to the Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic folder previously created.
A Read-Only Excel workbook titled SWedge Automation Template_Deterministic.xlsx will be automatically opened (if you have Excel installed on your local machine).
The SWedge Deterministic Input Data Automation Template Excel workbook and worksheets are protected to prevent any accidental modification to the tab structure and headers. The input Excel template contains six worksheets for inputting numerical parameters for automation.
Wedge ID | Slope | Upper Face | Rock Properties | |||
Dip | Dip Direction | Height | Dip | Dip Direction | Unit Weight | |
Wedge A | 65 | 185 | 33 | 12 | 185 | 0.026 |
Wedge B | 60 | 185 | 30 | 0 | 180 | 0.027 |
Wedge C | 70 | 180 | 10 | 20 | 180 | 0.025 |
The SLOPE worksheet should look like this:
Wedge ID | Joint 1 | ||||
Dip | Dip Direction | Waviness | C | Phi | |
Wedge A | 45 | 125 | 0 | 0 | 35 |
Wedge B | 30 | 120 | 0 | 0.1 | 30 |
Wedge C | 40 | 120 | 0 | 0.1 | 25 |
Wedge ID | Joint 2 | ||||
Dip | Dip Direction | Waviness | C | Phi | |
Wedge A | 70 | 225 | 0 | 0 | 35 |
Wedge B | 66 | 225 | 0 | 0 | 35 |
Wedge C | 60 | 225 | 0 | 0 | 35 |
The JOINTS worksheet should look like this:

We do not need to enter any data in the BASAL PLANE, FORCES, WATER, or SCALE WEDGE worksheets since those are not applicable.
We are now ready to automate computations in SWedge by reading from the input Excel file.
6.0 Automate from Excel
Return to the SWedge model.
The Automate Compute dialog allows you to add Excel input automation files to the queue, select an output format, and compute the results.
6.1 ADD FILES TO THE FILE QUEUE
To add multiple files to the File Queue:
- Select Automate from Excel
 from the Analysis menu to open the Automated Compute dialog.
from the Analysis menu to open the Automated Compute dialog.
Automate from Excel - Select the Open
 button to open a standard dialog to choose an Excel input file.
button to open a standard dialog to choose an Excel input file. - Navigate to the Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic folder and select the Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic_inputs.xlsx file.
You will see the Excel input file appear under the File Queue list box.
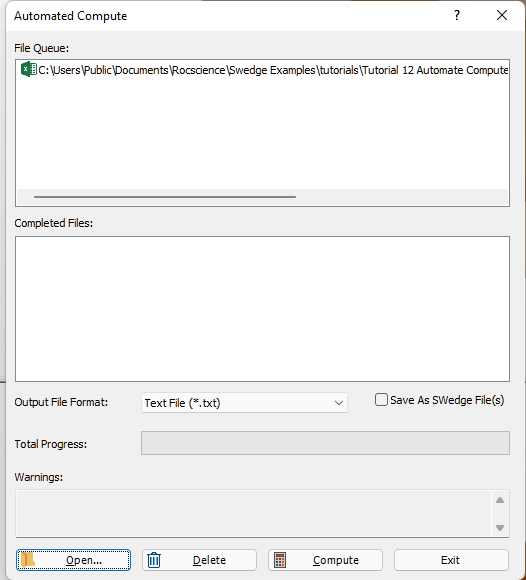
7.0 Output Result Files
Results files are automatically generated and saved into the same directory as the input Excel file after Automated Compute is complete. Before we run Compute, first ensure that the Output File Format is set to the desired format. Users can select from either Text File or Excel File format.
7.1 TEXT FILE FORMAT
While still in the Automated Compute dialog:
- Set the Output File Format dropdown to Text File.
- Select the Compute button to start the automated computing process.
- When all files have finished computing, select Exit to close the dialog.
The Total Progress can be seen at the bottom of the dialog. When files have finished computing, they will appear in the Completed Files list box.
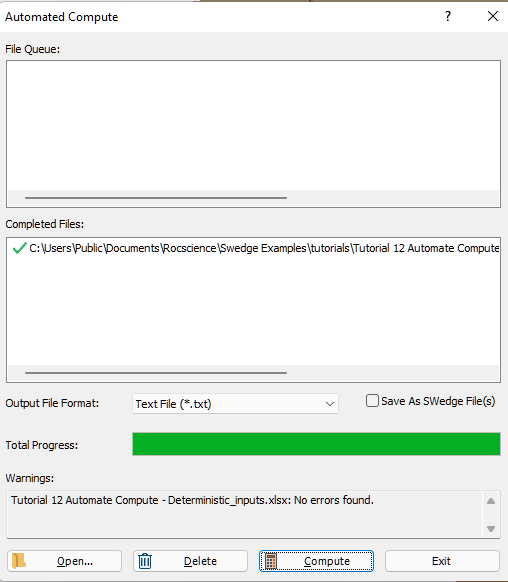
For each input Excel file, a text file (.txt) containing all results data is generated.
For a Deterministic Analysis (Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic_inputs.xlsx), the results data for all cases are outputted following the header row. Each row of data represents one analysis case (i.e., one wedge). Each data type is separated by a comma (,) for easy parsing.
- Take a look at the Results.txt result file.

7.2 EXCEL FILE FORMAT
Now, we will do the same as before, but this time we will generate the results as an Excel output file format.
- Select Automate from Excel
 from the Analysis menu to open the Automated Compute dialog.
from the Analysis menu to open the Automated Compute dialog. - Select the Open
 button to open a standard dialog to choose an Excel input file.
button to open a standard dialog to choose an Excel input file. - Navigate to the Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic folder and select the Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic.xlsx file.
- Set the Output File Format dropdown to Excel File.
- Select the Save As SWedge File(s) checkbox. This will save each automated compute case as an SWedge file.

Excel Output File Format - Select the Compute button to start the automated computing process.
- Since there are already Text File results in the results directory, a popup will appear with the message "Results folder(s) not empty. Duplicated results file(s) will be overwritten. Continue?". Select Yes.
- When all files have finished computing, select Exit to close the dialog.
You will see the Excel input file appear under the File Queue list box.
For each input Excel file, an Excel file (.xlsx) containing all results data is generated.
For a Deterministic Analysis (Tutorial 12 Automate Compute - Deterministic.xlsx), the results data for all cases are outputted following the header row. Each row of data represents one analysis case (i.e., one wedge). Each data type is separated by column.
- Take a look at the Results.xlsx result file.

- Take a look at each of the SWedge files generated:
- ResultsWedge A[0].swd7
- ResultsWedge B[1].swd7
- ResultsWedge C[2].swd7
- ResultsWedge A[0].swd7
8.0 Error Log
As you may have noticed, an Error Log is also generated for each input Excel file. For each input Excel file, an Error Log text file (Automate Compute Error Log.txt) is generated and saved into the same directory as the output file directories. Always check that the Error Log reports "No errors found" before post-processing the raw results data. If any errors do occur as a result of missing (i.e., blank cells) or invalid inputs, the Error Log will indicate which worksheet(s) and cell(s) are problematic.
This concludes the tutorial.